Which of the Following Best Describes Osteomalacia
Up to 3 tablets daily adjustment being made according to requirements. The NIH describes these forms of vitamin D.
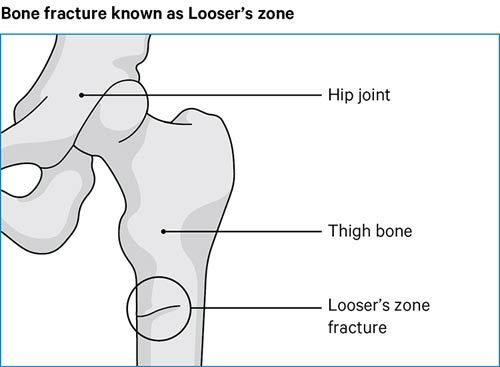
And may also result in osteomalacia referred to as rickets in pediatric patients andor osteoporosis with an increased risk for fractures see Warnings and Precautions 59 513.
. The two main types of vitamin D available from food are D2 and D3. The dose should be achieved by titration according to the following schedule Table 1. Anorexia is a medical term for a loss of appetiteWhile the term in non-scientific publications is often used interchangeably with anorexia nervosa many possible causes exist for a loss of appetite some of which may be harmless while others indicate a serious clinical condition or pose a significant risk.
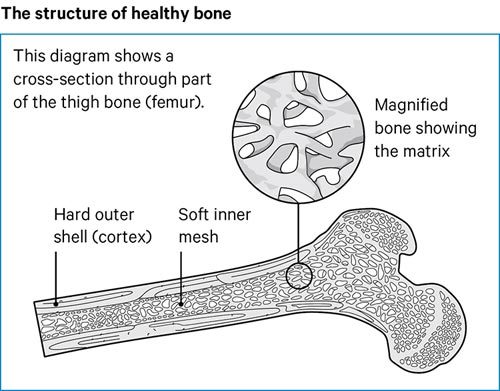
Fatty fish such as trout and mackerel and fish liver oil. Adults have more red marrow than children. Below is a text only representation of the Patient Information Leaflet.
Learn more about why it happens and how to prevent it here. Red marrow is the only site of blood formation in adults. Vitamin D resistant hypophosphateaemic osteomalacia.
PHOSPHATE SANDOZ should be dissolved in 13 to 12 a tumblerful of water 50-70ml and. CLEARING Clearing is the transition step between dehydration and infiltration with the embedding medium. Many dehydrants are.
In children it is located in the medullary. The Vitamin D and Omega 3 trial VITAL a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial following more than 25000 men and women ages 50 and older found that taking vitamin D supplements 2000 IUday for five years or vitamin D supplements with marine omega-3 fatty acids 1000 mgday reduced the incidence of autoimmune diseases by about 22 compared. B Most water is lost in breathing through the lungs.
In adults it is found in the cancellous bone spaces found in flat bones. It dehydrates rapidly causing little shrinkage or hardening and is possibly the best of the universal solvents. Sodium Calcium Iron.
Which of the following accurately describes water balance and recommended intakes. C The color of urine is used to diagnose a persons hydration status. Vitamin D resistant rickets.
The original leaflet can be viewed using the link above. For further information call emc accessibility on 0800 198 5000. Anorexia is a symptom not a diagnosis.
Up to 3 tablets daily adjustment being made according to requirements. An organic compound that is needed in small amounts in the diet to help regulate and support chemical reactions and. A Water intoxication is rare but can result in death.
D Liberal fluid intake 2 liters or more is recommended during times of heavy sweating. Rickets can cause a childs bones to soften and become prone to fractures and irregularities. Sodium Fiber Calcium Iron.
Vitamin D resistant hypophosphateaemic osteomalacia. A nutrient that yields no energy and is required in small amounts milligrams or micrograms per day is a Macronutrient Micronutrient. Children under 5 years.
The best examples of this type of joint are the sutures of the skull. E The first sign of dehydration is an. Vitamin D resistant rickets.
PHOSPHATE SANDOZ should be dissolved in 13 to 12 a tumblerful of water 50-70ml and. Which of the following are examples of micronutrients. Although tissues are water-free following dehydration infiltration with wax cannot be carried out because wax and ethanol are largely immiscible.
A one-year active-controlled study of pediatric patients treated with Topamax demonstrated. Children under 5 years. The text only version may be available in large print Braille or audio CD.
It can result from a vitamin D deficiency. The following statements are true regarding red bone marrow except.


0 Response to "Which of the Following Best Describes Osteomalacia"
Post a Comment